
There are many reasons why a dog may not instinctively engage in play with its human owners. For example, a dog kept in a kennel for breeding may have little positive interaction or experience with humans. A rescue dog may have been injured by its owner, or a puppy may simply be shy. If your dog or puppy is anxious or unwilling to engage with you, you can earn its trust through a slow, gentle process of socialization. Once your pet feels comfortable with you, it can learn to play and have fun.
While some dog owners might not care if their dog is playful, there are a number of benefits involved in dog and puppy play:
Patience is your most important tool. It can take time for a dog to start to trust its owners and even more time for it to learn appropriate ways to interact. Remember, though, that your goal is not to encourage your dog to do whatever it wants in whatever way suits it; rather, you are teaching it to interact with you following the rules and expectations that you'll want to set up.
So it's important to have a clear idea about boundaries and types of play that are acceptable to you. Be sure everyone working with your dog understands your goals, rules, and expectations. For example, your housemate may think it's cute when your dog growls while holding a toy in its mouth while you have set a rule that growling is unacceptable. Naturally, different sets of rules and different types of play will be confusing to your new pet.
There are several reasons a dog may not have learned to play. One common reason is a lack of early socialization. Some dogs don't play simply because no one has ever engaged in a game with them. Another reason is that their instincts may drive them to do other things. For instance, a border collie may have the drive to herd your children together in the yard rather than engage in a game of fetch.
No matter why your dog isn't playing, you should begin by slowly introducing it to toys and games. Start by leaving the toys around to sniff and get used to, rather than immediately trying to engage in an all-out game of tug-of-war. An improperly socialized dog may be scared if you move too fast, and a dog whose instincts are pushing it to do something else will just be confused.
Start off with soft praise or a treat for any interest your dog shows in toys. You can even hide a treat or spread a little peanut butter on a tug toy or a ball. Your dog will quickly learn that toys mean good things happen.
Once your dog is comfortable with the toys, it's time to start interacting with it. Again, start off slow. Sit close to your dog and roll a ball toward it or shake a tug toy a little. If it shows interest, give it a treat and praise. It may take some time, but the more you engage your dog in play, the sooner it will learn what's expected. Before you know it, your dog will be playing as if it's done it all its life.
Sometimes teaching a dog to play involves more than simply slowly introducing it to the idea. Games like fetch, for instance, have more than one part. It might be easy to teach your dog to run and pick up a ball you throw, but it'll have to know "come" and "drop it" in order for the game to continue smoothly without turning into a game of chase. If your dog is having trouble playing, make sure it knows the basic commands involved in playing the game.
Not every dog is going to like every kind of game. Try to choose games that best suit your dog's personality. A retriever is likely to enjoy a game of fetch. A terrier might really get into a game of tug-of-war. Herding dogs, such as border collies and Australian shepherds, tend to do well at agility and Frisbee. By matching the games you choose to suit the things your dog was bred to do (retrieving or herding, for example), it'll be easier to teach your dog to play, and a lot more fun for your dog.
Proofing is the process by which you ensure that your dog can keep up new behaviors in a variety of settings and situations. It's not easy for a dog to play properly when it's in a new, exciting setting or playing with unfamiliar people or animals.
To proof your dog's new play skills, you'll want to place it in a variety of situations to see how well it retains its training.
If you discover that your dog hasn't really internalized the rules of play, you may need to go back to earlier steps in the process.
For this type of training, patience is key; if you move too quickly, you may lose your dog's trust.

Tetanus in Dogs
Tetanus is an infection caused by bacteria found in soil. It can cause severe symptoms in dogs and even lead to death if not treated promptly.
8 Common Dog Paw Problems
It is important to check your dog’s paws regularly for any issues and take steps to keep them healthy and protected.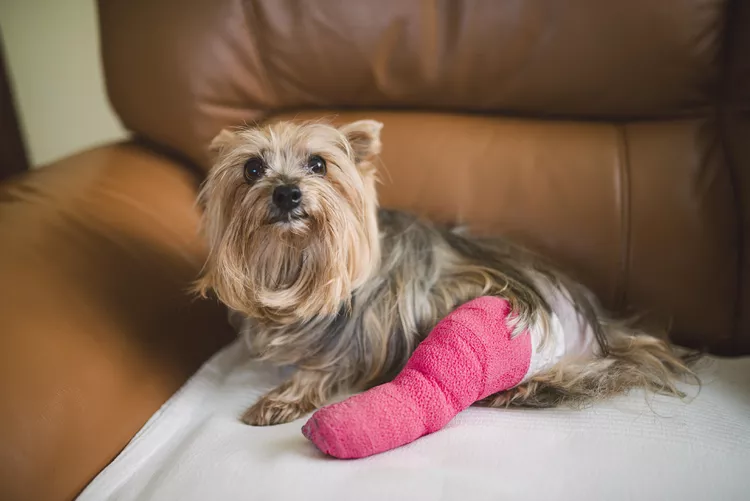
Common Injuries in Dogs and How to Treat Them
Learn about the most common injuries in dogs—whether in their legs, spine, tail, or eye—and how you should treat them with this helpful list.
Can Cats Eat Strawberries? How to Safely Share This Summer Berry
Although cats are primarily meat eaters, strawberries may be an interesting and tasty snack for your feline friend. Find out the risks of feeding strawberries to cats and how to safely let your cat enjoy this fruit.
Is Shrimp Bad For Dogs?
Shrimp can be a healthy, nutritional food for people but can dogs eat them, too? What are the main concerns with feeding shrimp to your dog?
Dog Food Basics
Are you feeding your dog the best way possible? Check out these dog feeding tips to keep your dog healthy and happy.
Rhodesian Ridgeback: Dog Breed Characteristics & Care
The Rhodesian ridgeback is a large hunting dog with a high prey drive. Learn about the breed's history, exercise needs, and more.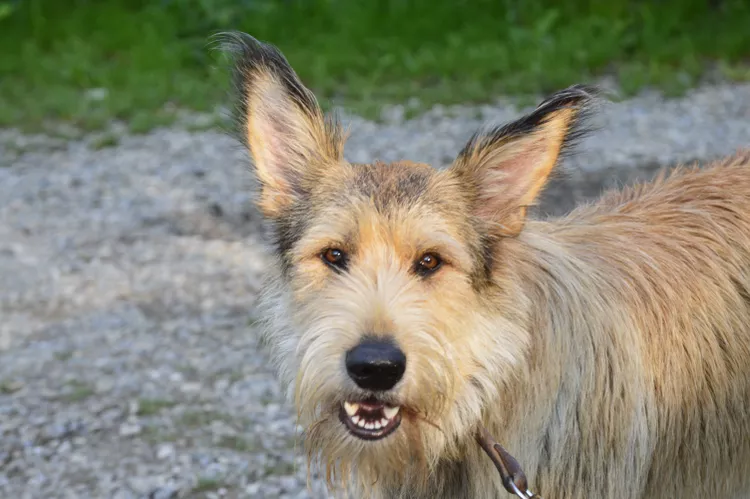
Berger Picard: Dog Breed Characteristics & Care
The Berger Picard is a French herding dog with a friendly smile and shaggy beard. Learn about its history, health, exercise needs, and more.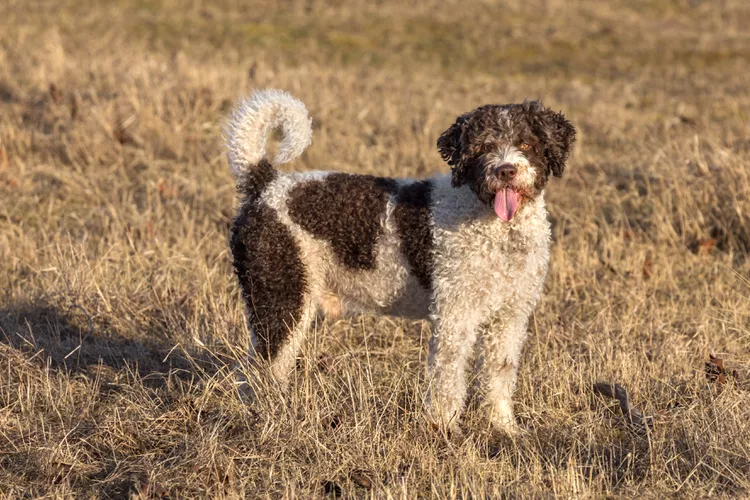
Spanish Water Dog: Breed Characteristics & Care
In the hands of an expert owner, the Spanish water dog shines as an active and faithful companion. Learn about its history, training, and more.
Cat Bunting Behavior: What Does It Mean?
Cats rub their heads against prominent objects to leave scent markings as a part of scent communication.
How to Train Your Cat to Stop Urine Marking
Most male (and some female) house cats will mark territory at some point. Learn the causes or cat urine marking and how to prevent this annoying behavior.
7 Reasons Why Cats Love Bathrooms
Why do cats follow you to the bathroom? Many cats—strangely enough—love the bathroom! Find out why cats seem to love bathrooms so much.
Leptospirosis in Cats
Leptospirosis is rare but potentially fatal in cats. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention.
Ear Infections in Cats
An ear infection must be treated based on the source of irritation, which may be internal or external. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention.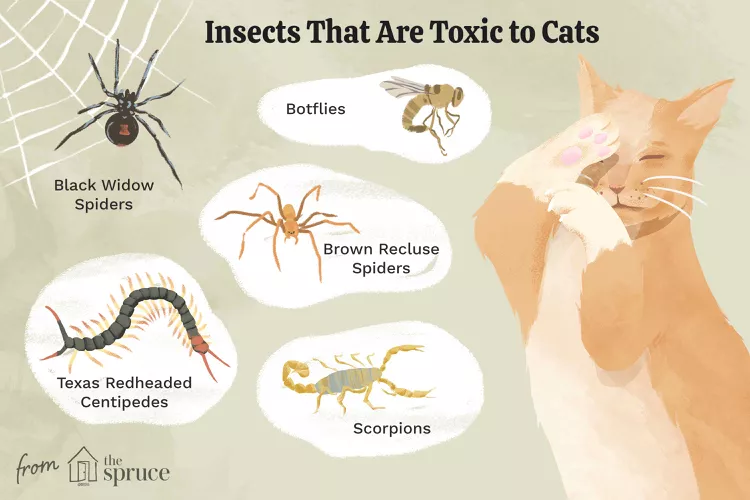
Insects That Are Toxic to Cats
Can cats eat bugs? Some bugs can cause injury or illness to your cat, while others are relatively harmless.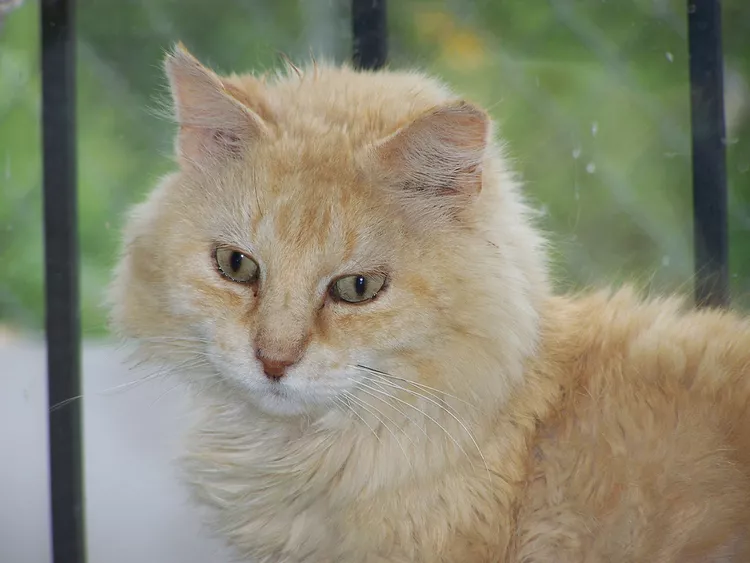
Testing for Contagious Feline AIDS (FIV)
Cats should be tested for the contagious feline immunodeficiency virus or FIV. Cats that are positive for the virus usually live normal lives.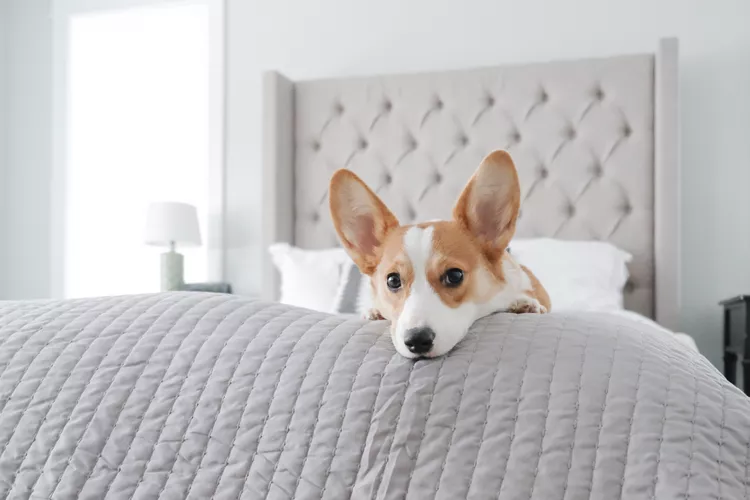
Why Does My Dog Pee on My Bed?
Is your dog peeing on your bed? Find out why your dog is having urinary accidents on the bed and learn what to do about it—plus how to stop the habit.
Why Almost Any Dog Can Do Agility Training
Why Almost Any Dog Can Do Agility Training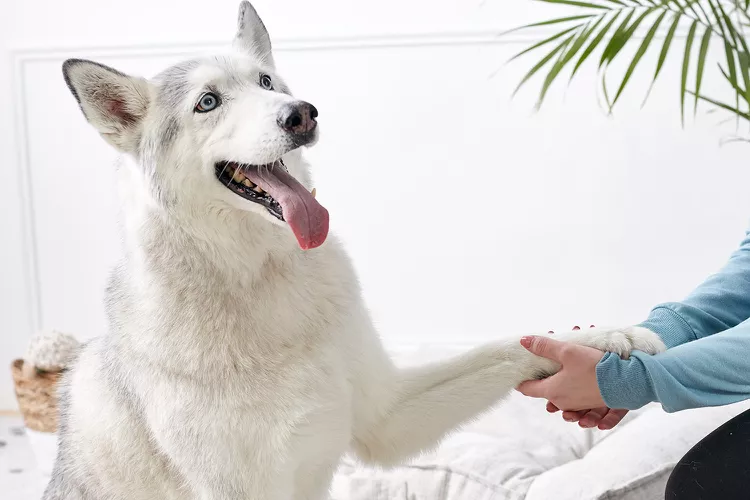
How to Train Your Dog to Shake Paws
Shaking paws is a fun dog trick that most dogs pick up rather quickly Learn how to train your dog to shake in just a few simple steps.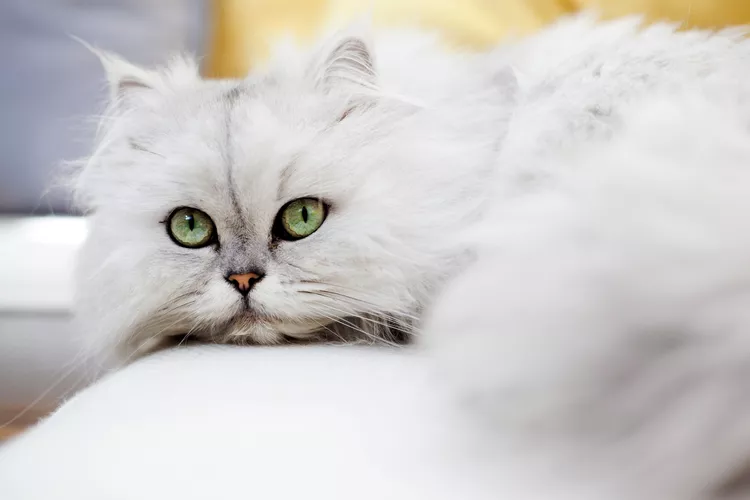
14 Asian Cat Breeds And Their Rich Hiss-tories
Find out more about the cat breeds that originated from Asia. Some breeds include the Persian, Oriental shorthair, and Japanese bobtail.