
Luxating patella, the technical term for a kneecap popping out of place, creates instability in a cat's hind leg by reducing the functionality of the knee joint. It causes varying degrees of pain and immobility. Luxating patella can occur as a result of trauma or aging, and it can lead to arthritis if untreated. While any cat can experience this problem, Devon Rex and Abyssinian cats may have a genetic predisposition for unstable knee caps.
Luxating patella is an orthopedic condition in which a cat's knee cap (patella) slips out of place. The patella is a small bone beneath the patellar ligament that sits in a groove in the femur called the trochlear groove. When the knee is bent and flexed, the patella rides up and down in the trochlear groove. If the kneecap is not functioning properly, it may luxate—or pop in and out of the groove.
When a cat's kneecap is out of place, bending and flexing the knee joint are uncomfortable. This makes walking, running, and jumping painful and difficult for the cat. If both knees are affected, each side may have a different degree of severity.
Luxating patella affects a cat's rear legs only (its front legs don't have "knees"). The symptoms are those of pain and instability. A popping sound when the cat walks may indicate a loose patella, and the bone may feel wobbly or loose when touched. Because cats try to heal themselves by licking or chewing a painful problem area, these behaviors may indicate that something is wrong with the knee(s).
Cats with patellar luxation may experience symptoms on and off. If the kneecap is in its proper location, the cat will be able to walk, run, and jump normally. When the kneecap is out of place, the cat will suddenly experience pain and limited mobility in the affected knee.
It's possible for a cat to have a low-grade luxating patella and no symptoms. Your vet may discover this during a routine wellness exam and advise you to keep an eye on it.
The exact cause of patellar luxation is unknown, but potential contributing factors include:
It's important to visit your vet if your cat is limping. The vet will begin by reviewing your cat's medical history and performing an examination.
Patellar luxation is diagnosed by a veterinarian after palpating the knee joint and ruling out other causes for the abnormality. X-rays may be necessary to rule out other issues and confirm a diagnosis. The vet may discover a luxating patella in one or both knees.
The luxation is often medial, meaning it dislocates towards the inside of the knee. Or, the luxation may be lateral, meaning it dislocates to the outside of the knee.
The diagnosis of a luxating patella will fall into one of four categories based upon the severity of the dislocation:
Luxating patella in cats is often treated conservatively at first. Your vet may recommend rest and exercise restriction, which means you'll need to limit your cat's access to running and jumping. Anti-inflammatory medications may also be prescribed for a short time.
If the patellar luxation is mild (Grade I), your cat will rarely experience discomfort. In mild to moderate cases (Grade II), you may see signs on and off when the kneecap occasionally goes out of the groove. In mild cases, the cat should be able to live a relatively normal life. Rest and medications may be needed from time to time if the knee issues reappear.
If conservative therapy is not effective and your cat is experiencing frequent pain and immobility, then surgical treatment may be necessary. This is often the case with Grade III and IV patellar luxation.
Surgery for patellar luxation involves correcting the conditions that make the patella dislocate. There are several surgical techniques for the repair of patellar luxation. Surgery generally involves the deepening of the trochlear groove, reconstruction of the soft tissues around the patella, and sometimes reshaping of abnormal bones.
Recovery from surgery requires rest and pain management at first. Most cats recover quickly but may benefit from some type of gentle physical therapy.
Though it is possible to reinjure the knee joint, most cats will not experience future problems.
You cannot completely avoid patellar luxation in your cat, but you can reduce the risk. If your cat likes to jump up to high places, create lower steps to minimize stress on the knees.
Cats diagnosed with luxating patella should never be bred to prevent passing on problematic genes.

Tetanus in Dogs
Tetanus is an infection caused by bacteria found in soil. It can cause severe symptoms in dogs and even lead to death if not treated promptly.
8 Common Dog Paw Problems
It is important to check your dog’s paws regularly for any issues and take steps to keep them healthy and protected.
Common Injuries in Dogs and How to Treat Them
Learn about the most common injuries in dogs—whether in their legs, spine, tail, or eye—and how you should treat them with this helpful list.
Can Cats Eat Strawberries? How to Safely Share This Summer Berry
Although cats are primarily meat eaters, strawberries may be an interesting and tasty snack for your feline friend. Find out the risks of feeding strawberries to cats and how to safely let your cat enjoy this fruit.
Is Shrimp Bad For Dogs?
Shrimp can be a healthy, nutritional food for people but can dogs eat them, too? What are the main concerns with feeding shrimp to your dog?
Dog Food Basics
Are you feeding your dog the best way possible? Check out these dog feeding tips to keep your dog healthy and happy.
Rhodesian Ridgeback: Dog Breed Characteristics & Care
The Rhodesian ridgeback is a large hunting dog with a high prey drive. Learn about the breed's history, exercise needs, and more.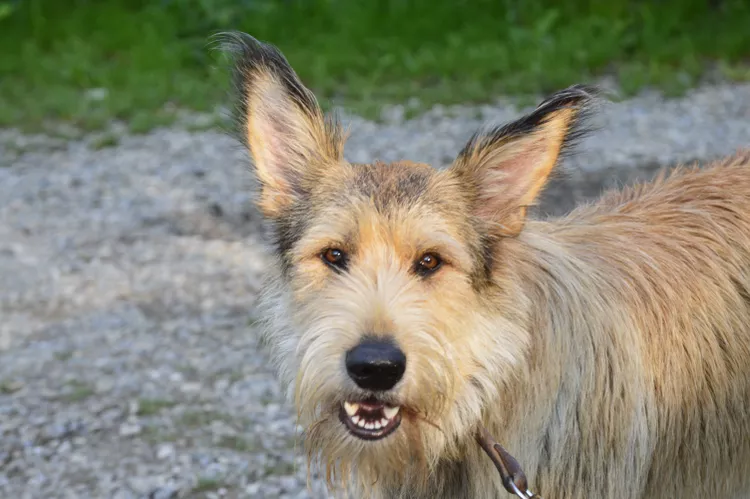
Berger Picard: Dog Breed Characteristics & Care
The Berger Picard is a French herding dog with a friendly smile and shaggy beard. Learn about its history, health, exercise needs, and more.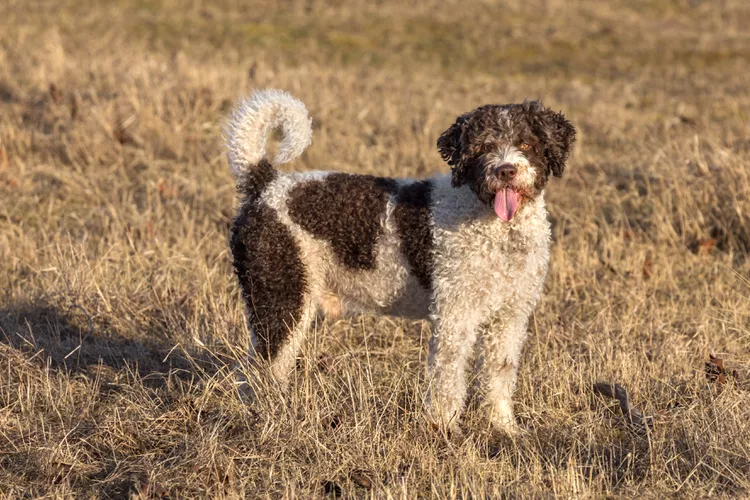
Spanish Water Dog: Breed Characteristics & Care
In the hands of an expert owner, the Spanish water dog shines as an active and faithful companion. Learn about its history, training, and more.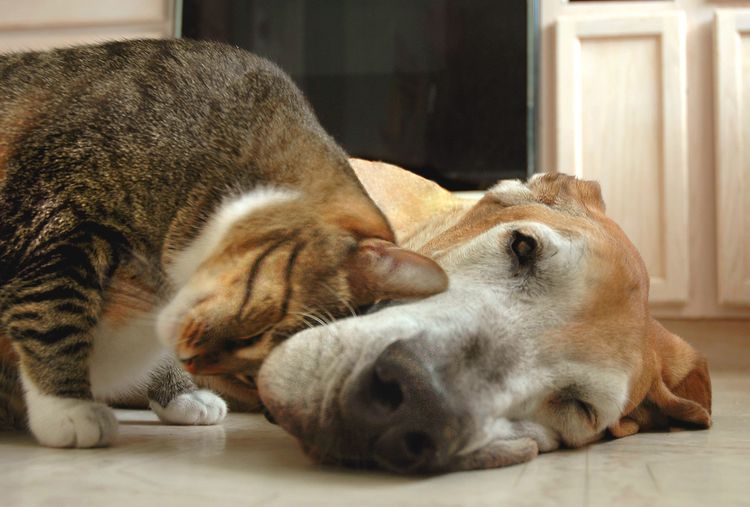
Cat Bunting Behavior: What Does It Mean?
Cats rub their heads against prominent objects to leave scent markings as a part of scent communication.
How to Train Your Cat to Stop Urine Marking
Most male (and some female) house cats will mark territory at some point. Learn the causes or cat urine marking and how to prevent this annoying behavior.
7 Reasons Why Cats Love Bathrooms
Why do cats follow you to the bathroom? Many cats—strangely enough—love the bathroom! Find out why cats seem to love bathrooms so much.
Leptospirosis in Cats
Leptospirosis is rare but potentially fatal in cats. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention.
Ear Infections in Cats
An ear infection must be treated based on the source of irritation, which may be internal or external. Learn the causes, treatment, and prevention.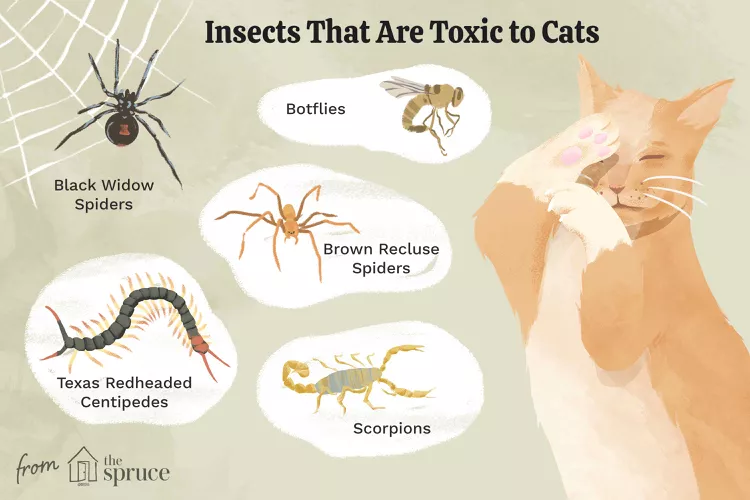
Insects That Are Toxic to Cats
Can cats eat bugs? Some bugs can cause injury or illness to your cat, while others are relatively harmless.
Testing for Contagious Feline AIDS (FIV)
Cats should be tested for the contagious feline immunodeficiency virus or FIV. Cats that are positive for the virus usually live normal lives.
Why Does My Dog Pee on My Bed?
Is your dog peeing on your bed? Find out why your dog is having urinary accidents on the bed and learn what to do about it—plus how to stop the habit.
Why Almost Any Dog Can Do Agility Training
Why Almost Any Dog Can Do Agility Training
How to Train Your Dog to Shake Paws
Shaking paws is a fun dog trick that most dogs pick up rather quickly Learn how to train your dog to shake in just a few simple steps.
14 Asian Cat Breeds And Their Rich Hiss-tories
Find out more about the cat breeds that originated from Asia. Some breeds include the Persian, Oriental shorthair, and Japanese bobtail.